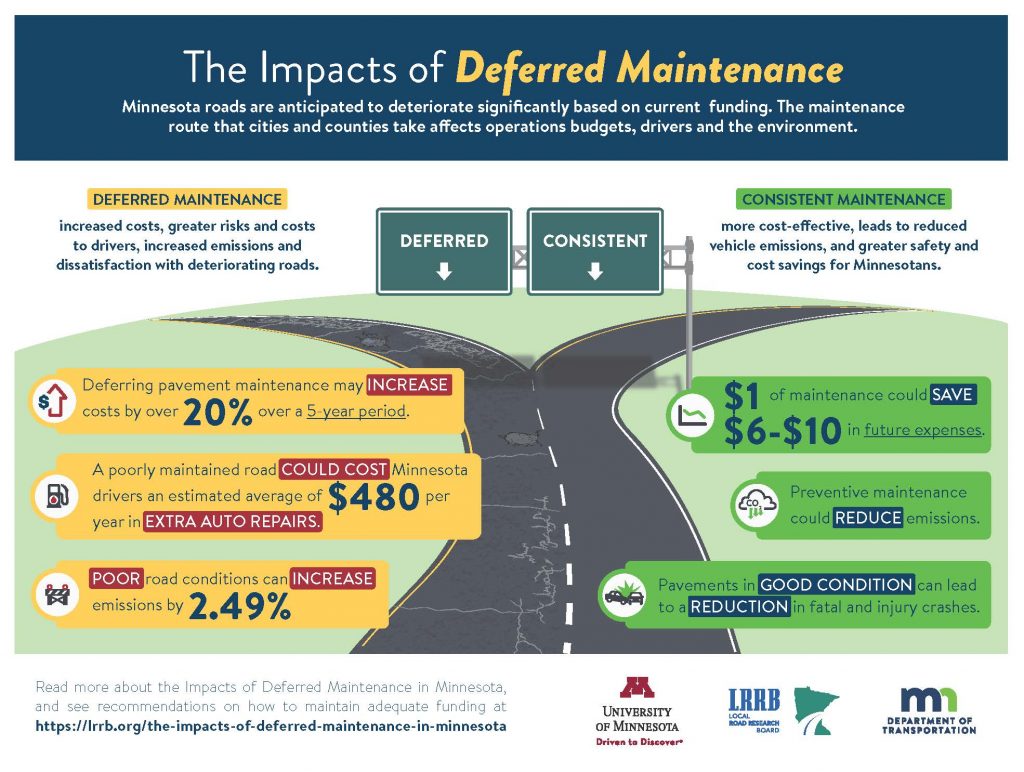
Rising construction costs and declining funding have created an estimated deficit of $17.7 billion for state roads over the next 20 years. The inability to maintain roads and bridges in good condition leads to shortened infrastructure life spans and higher future repair costs.
As upkeep is postponed, the necessary road work grows and material costs increase, resulting in higher future maintenance costs. New research sponsored by the Local Road Research Board identifies factors that impact maintenance spending, examines how investment decisions are made and provides recommendations to help local governments close maintenance funding gaps.
The research team examined maintenance spending across Minnesota localities, developed case studies and conducted a survey in which representatives from 31 local governments in Minnesota described the size and condition of their roadway networks, challenges with managing maintenance investments, funding gaps, and strategies they use to minimize deferred maintenance. The researchers suggest that cities and counties coordinate road maintenance activities; adopt a standard definition of deferred maintenance; and, most importantly, thoroughly monitor and report road conditions, trends and achievements toward targets to keep the public and budget decision-makers well-informed.